When it comes to air purification, HEPA filters are often touted as the gold standard. They are highly effective at removing airborne particles, but have you ever wondered what size particle a HEPA filter can capture?
In this article, we’ll delve into the world of HEPA filters, exploring their capabilities, limitations, and the importance of particle size in air filtration.
What Is a HEPA Filter?

HEPA stands for High Efficiency Particulate Air. A HEPA filter is a type of mechanical air filter that is designed to trap and remove tiny particles from the air. These particles can include dust, pollen, pet dander, mold spores, and even bacteria and viruses. HEPA filters are commonly used in air purifiers, vacuum cleaners, and HVAC systems to improve indoor air quality.
How Does a HEPA Filter Work?
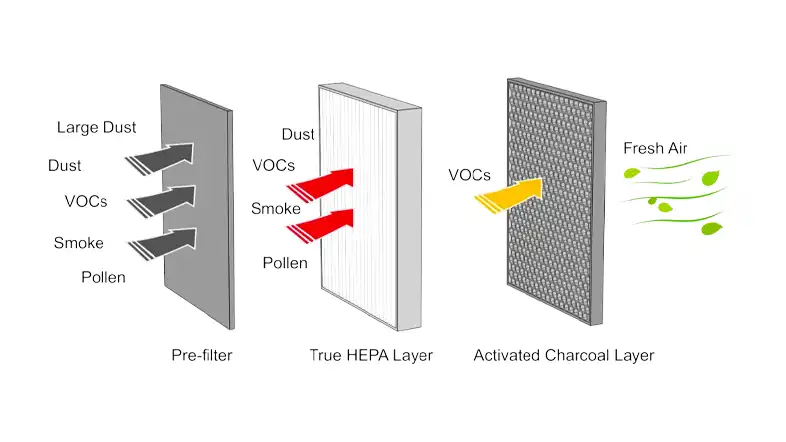
HEPA filters work through a combination of diffusion, interception, and impaction. As air flows through the filter, particles are forced to change direction multiple times due to the filter’s fibrous material. This process causes the particles to collide with the fibers and become trapped, effectively removing them from the air.
HEPA Filter Particle Size

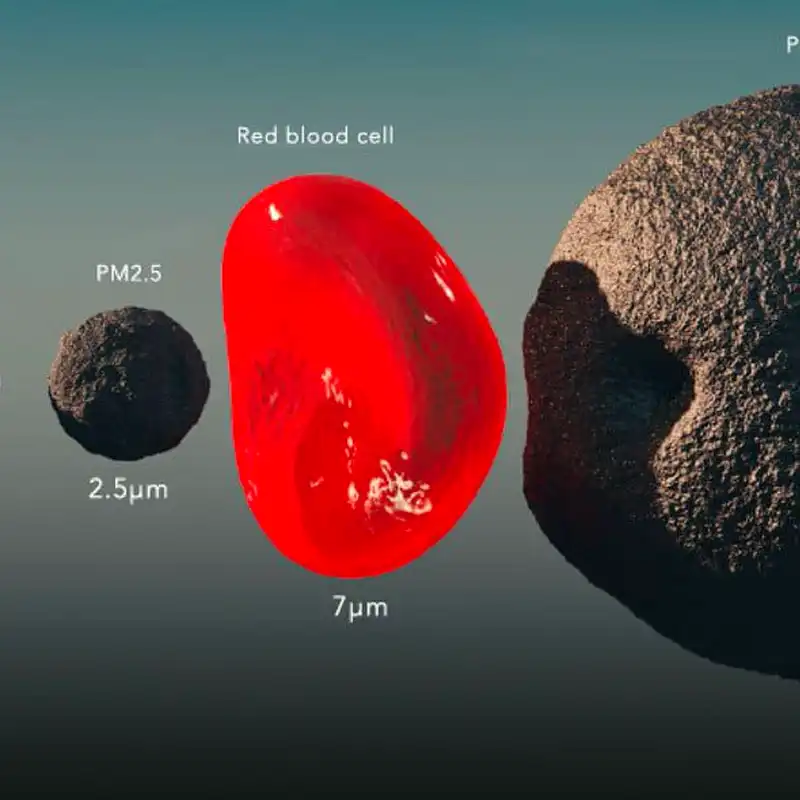
To comprehend what size particle a HEPA filter can capture, it’s essential to understand particle size measurement. Particles are categorized based on their diameter, and they are typically measured in micrometers (µm). The human eye can only see particles larger than 40 µm, which means many harmful particles are invisible to us.
Here’s a table summarizing the effectiveness of HEPA filters at capturing particles of different sizes:
| Particle Size | HEPA Filter Capture Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Larger than 0.3 microns | Highly Effective (often close to 100%) |
| 0.3 microns | 99.97% Efficiency (most penetrating particle size) |
| Smaller than 0.3 microns | Effective (capturing a significant percentage) |
This table illustrates that HEPA filters are highly effective at capturing particles larger than 0.3 microns, moderately effective at capturing particles around 0.3 microns (the most penetrating particle size), and still effective at capturing smaller particles. The 0.3-micron size is often used as a reference point because it’s where HEPA filters achieve their minimum efficiency, yet it’s a very challenging size to capture for most air filters.
The HEPA Filter Standard
The HEPA filter standard is defined by the U.S. Department of Energy. For a filter to be classified as HEPA, it must remove 99.97% of particles that are 0.3 µm in size. This standard is particularly stringent, as it targets particles that are smaller and more challenging to capture.
Why Particle Size Matters
Particle size matters because different particles pose varying health risks. Ultrafine particles, which are smaller than 0.1 µm, can penetrate deep into the respiratory system and may lead to various health issues. HEPA filters excel in capturing particles within the 0.3 µm range, which includes most allergens, dust, and common pollutants.
What Size Particles Does a Hepa Filter Remove

HEPA filters excel at removing a wide range of particles, making them a popular choice for improving indoor air quality. Some common airborne contaminants that HEPA filters can remove include:
- Dust mites
- Pollen
- Mold spores
- Pet dander
- Bacteria
- Smoke particles
- Viruses (including some strains of the flu)
These filters effectively trap these particles, preventing them from circulating in the air you breathe.
HEPA Filters vs. Small Particles
HEPA filters are exceptionally effective at capturing small particles. They can trap particles as small as 0.3 µm, making them ideal for improving indoor air quality in homes, offices, and healthcare facilities.
HEPA Filters vs. Large Particles
While HEPA filters are excellent at capturing small particles, they may not be as efficient at removing larger particles like dust mites or pollen. For these larger particles, pre-filters or combination filters are often used in conjunction with HEPA filters for comprehensive filtration.
HEPA Filters in Different Settings
HEPA filters find applications in various settings. They are commonly used in healthcare settings to control the spread of infectious diseases, in cleanrooms for semiconductor manufacturing, and in homes to reduce allergens and improve respiratory health.
Does Hepa Filter Remove Smoke Particles

Yes, HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are effective at removing smoke particles from the air. Smoke particles consist of tiny solid and liquid particles, including those produced by tobacco smoke, wildfire smoke, and other sources.
HEPA filters are designed to capture particles as small as 0.3 microns in size and are very efficient at trapping fine particles, which include most smoke particles.
HEPA filters work by using a dense network of fibers to physically trap particles that pass through them. Smoke particles, even those smaller than 0.3 microns, get caught in the filter’s fibers through mechanisms like diffusion and electrostatic attraction. The key to their effectiveness is their ability to capture a wide range of particle sizes.
However, it’s important to note that while HEPA filters are excellent at removing the particulate matter found in smoke, they may not be as effective at eliminating the odor associated with smoke. Smoke odors are often caused by volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other gases, which are typically smaller than the 0.3-micron particle size that HEPA filters are optimized to capture. To address the odor associated with smoke, you may need to use additional filtration methods such as activated carbon filters or air purifiers with specialized odor-removing technologies.
HEPA filters are indeed effective at removing smoke particles from the air, but they may not fully address the odor issue caused by smoke. For comprehensive smoke removal, consider air purifiers that combine HEPA filtration with activated carbon or other odor-reducing technologies.
Hepa Filter Efficiency vs Particle Size
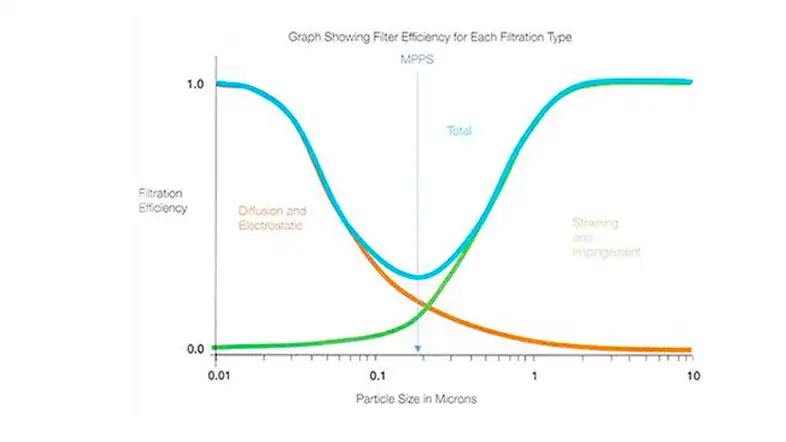
HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filter efficiency varies with the particle size being filtered. HEPA filters are most efficient at capturing particles of a specific size, typically particles around 0.3 microns in diameter. Here’s a breakdown of HEPA filter efficiency concerning different particle sizes:
- Particles Larger than 0.3 Microns: HEPA filters are highly effective at capturing larger particles, including dust, pollen, pet dander, and most bacteria. The efficiency for particles larger than 0.3 microns is often close to 100%.
- 0.3 Micron Particles: This is often considered the most penetrating particle size. HEPA filters are required to capture at least 99.97% of particles that are precisely 0.3 microns in size. This size represents a challenge for HEPA filters, but they are designed to be highly efficient at capturing particles of this size.
- Particles Smaller than 0.3 Microns: HEPA filters are still effective at capturing a significant percentage of particles smaller than 0.3 microns, thanks to mechanisms like diffusion and electrostatic attraction. While their efficiency may decrease for smaller particles, they can still capture a considerable portion of them.
The efficiency of HEPA filters is impressive for a broad range of particle sizes. They are particularly renowned for their ability to trap particles that are both larger and smaller than the 0.3-micron mark. The 0.3-micron size is used as a reference point because it represents the most challenging particle size for HEPA filters to capture while maintaining their high efficiency.
Here’s a table summarizing HEPA filter efficiency at various particle sizes:
| Particle Size | HEPA Filter Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Larger than 0.3 microns | Highly Effective (often close to 100%) |
| 0.3 microns | At least 99.97% Efficiency (most challenging size) |
| Smaller than 0.3 microns | Effective (capturing a significant percentage) |
This table illustrates how HEPA filters are highly efficient at capturing particles both larger and smaller than the 0.3-micron size, with their efficiency peaking at the 0.3-micron particle size, which is considered the most challenging size for them to capture while maintaining their high standards.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HEPA filters are highly effective at capturing particles as small as 0.3 µm, making them an excellent choice for improving indoor air quality. Understanding particle size and the HEPA filter standard is essential for selecting the right filter for your needs.
FAQs
Are HEPA filters effective against viruses?
HEPA filters can capture some viruses, but not all. They are most effective against larger particles, so additional measures may be needed for comprehensive virus filtration.
Do HEPA filters remove bad odors?
HEPA filters are not designed to remove odors. For odor removal, consider using activated carbon filters or other specialized filtration methods.
Can I wash and reuse HEPA filters?
HEPA filters are typically not washable and should be replaced according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Do HEPA filters produce ozone or other harmful byproducts?
HEPA filters do not produce ozone or harmful byproducts. They are considered safe for air purification.
Are there HEPA filters for cars?
Yes, there are HEPA filters designed for use in vehicles, which can help improve air quality inside your car.




