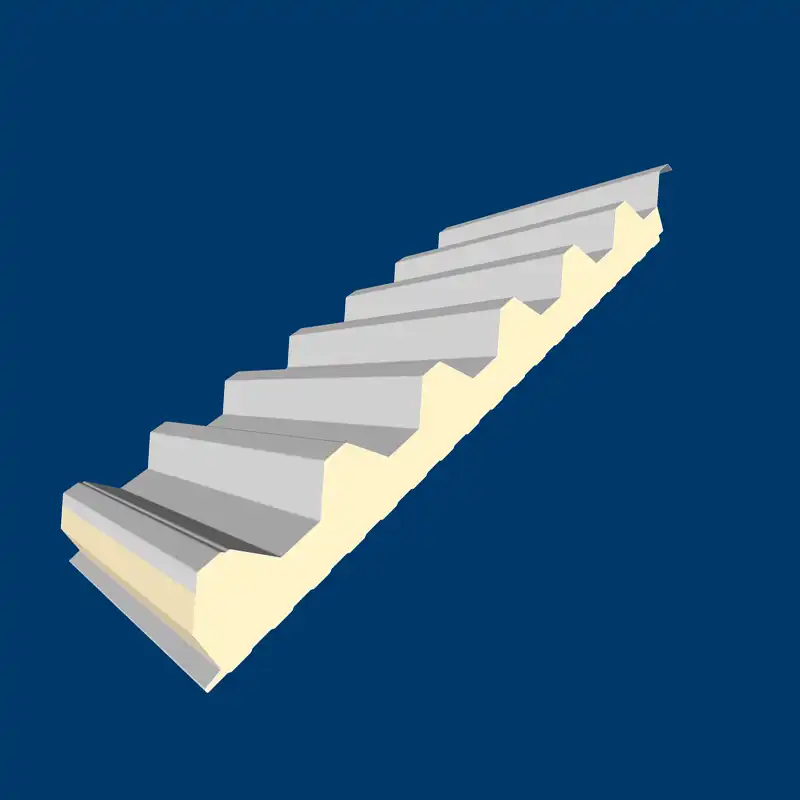
In the realm of modern construction, Sandwich Panel Profiles stand as a cornerstone for achieving optimal structural integrity and thermal efficiency. These profiles, composed of layers with varying materials, are revolutionizing the way buildings are designed and constructed.
This is the ultimate guide to the sandwich panel profile in the following:
What Is Sandwich Panel Profile
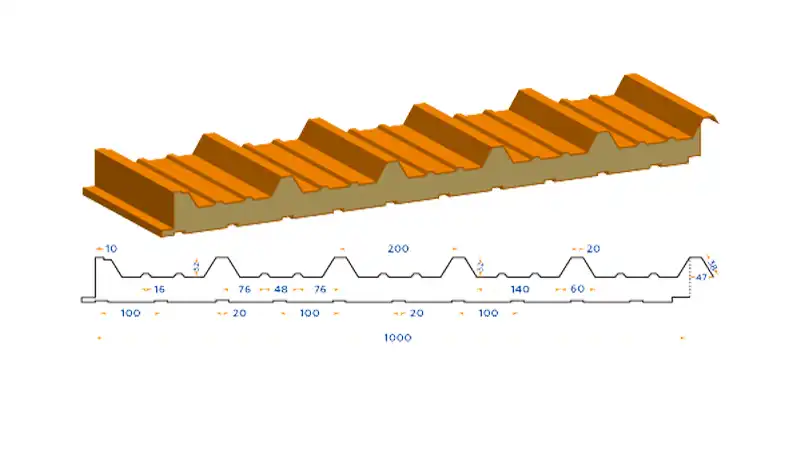
The term “Sandwich Panel Profile” refers to a specialized construction material commonly used in the building industry. Essentially, it is a composite material that consists of three layers – two outer layers and a core material in between, resembling a sandwich.
The outer layers, often made of metal or other rigid materials, provide structural support, while the core material, usually an insulating substance like polyurethane (PU), polyisocyanurate (PIR), or mineral wool, enhances the panel’s thermal properties.
These panels are designed to offer a combination of strength, insulation, and lightweight construction. The unique structure of sandwich panels makes them a popular choice for various construction applications, ranging from residential buildings to industrial facilities.
Types of Sandwich Panel Profiles
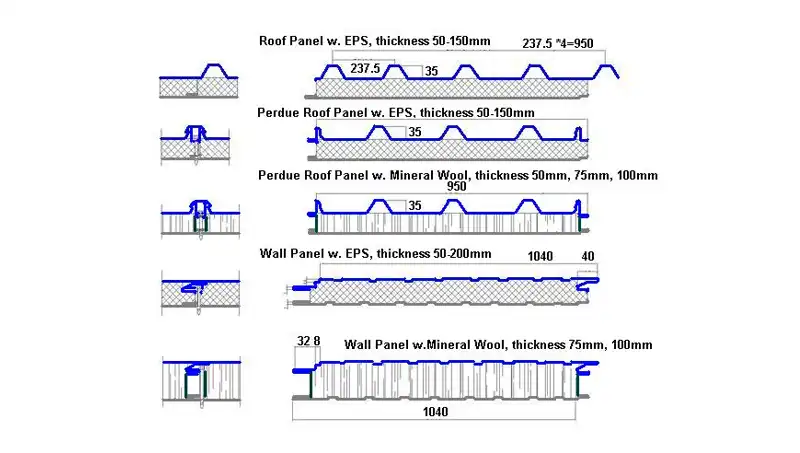
Polyurethane (PU) Profiles
PU profiles offer excellent insulation properties and are widely utilized in residential and commercial applications. Their versatility makes them a popular choice for various construction projects.
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Profiles
Known for their high fire resistance and enhanced thermal performance, PIR profiles are preferred in structures where safety and energy efficiency are paramount considerations.
Mineral Wool Profiles
Mineral wool profiles, made from natural or synthetic fibers, provide robust fire resistance and sound insulation. They find applications in industrial settings where these properties are crucial.
Advantages of Sandwich Panel Profiles
Thermal Insulation
The layered construction of sandwich panels, often filled with insulating materials, ensures superior thermal performance. This results in energy-efficient buildings and reduced heating and cooling costs.
Structural Strength
Sandwich panels offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios, contributing to the structural integrity of buildings. This characteristic makes them suitable for a wide range of construction projects.
Lightweight Construction
The lightweight nature of sandwich panels not only facilitates easier handling during installation but also minimizes the overall load on the building structure. This is particularly beneficial in seismic-prone areas.
Applications of Sandwich Panel Profiles
Sandwich panel profiles find a wide array of applications across various sectors due to their versatile nature and numerous benefits. Let’s explore some of the key applications of these innovative construction materials:
Residential Buildings:
Sandwich panels are frequently used in residential construction for walls, roofs, and floors. Their excellent insulation properties contribute to energy-efficient homes, providing comfort to residents while minimizing energy consumption.
Commercial Structures:
Offices, shopping malls, and other commercial buildings benefit from the structural strength and thermal insulation offered by sandwich panel profiles. They contribute to creating comfortable and sustainable spaces for businesses and customers.
Industrial Facilities:
The lightweight yet sturdy nature of sandwich panels makes them ideal for industrial constructions. Warehouses, manufacturing plants, and storage facilities often use sandwich panels for walls and roofing, ensuring both insulation and durability.
Cold Storage Facilities:
Sandwich panels are well-suited for cold storage applications, such as refrigerated warehouses and freezers. Their insulation capabilities help maintain controlled temperatures, essential for preserving perishable goods.
Educational Institutions:
Schools and universities benefit from sandwich panel profiles in constructing classrooms and administrative buildings. The panels contribute to creating energy-efficient and comfortable learning environments.
Healthcare Facilities:
Hospitals and medical facilities often use sandwich panels to ensure a controlled and comfortable indoor environment. The insulation properties aid in maintaining optimal temperatures for patient comfort and medical equipment.
Agricultural Buildings:
Farm structures like barns, poultry houses, and agricultural storage facilities benefit from sandwich panel profiles. They offer durability, insulation, and resistance to environmental conditions.
Data Centers:
Data centers require a controlled environment to ensure the optimal functioning of electronic equipment. Sandwich panels, with their thermal insulation properties, contribute to maintaining stable temperatures in these critical facilities.
Sports Arenas and Recreational Centers:
The adaptability of sandwich panels makes them suitable for constructing sports facilities. From arenas to gymnasiums, these panels provide a combination of structural integrity and energy efficiency.
Prefab Construction:
Sandwich panels are commonly used in prefabricated construction methods. Their ease of transportation, quick installation, and energy-efficient properties make them a preferred choice for modular and prefab buildings.
Telecommunication Shelters:
Shelters housing telecommunication equipment benefit from the durability and weather resistance of sandwich panels, ensuring the protection of sensitive electronic components.
Renovation Projects:
Sandwich panels are increasingly used in renovating existing structures. They offer a quick and effective solution to enhance insulation and structural integrity without extensive modifications.
The diverse applications of sandwich panel profiles underscore their importance in modern construction, playing a pivotal role in creating sustainable, energy-efficient, and resilient structures across various sectors.
Consideration of Material Selection
When choosing sandwich panel materials, factors such as thermal resistance, environmental impact, and durability must be carefully considered. Sustainable options are gaining traction in response to the growing emphasis on eco-friendly construction.
When it comes to sandwich panel profiles, careful consideration of material selection is paramount to ensuring optimal performance and meeting specific project requirements. The choice of materials influences factors such as thermal insulation, structural integrity, and overall sustainability.
Here are key aspects to consider:
Thermal Resistance:
Different core materials offer varying degrees of thermal resistance. For example, polyurethane (PU) and polyisocyanurate (PIR) are known for high thermal insulation properties, making them suitable for applications where energy efficiency is crucial.
Structural Strength:
The outer layers of sandwich panels are typically made from materials like metal or other rigid substances. Consider the structural requirements of the project and choose outer layers that provide the necessary strength and durability.
Environmental Impact:
Increasing emphasis on sustainability has led to the development of eco-friendly sandwich panel materials. Consider materials with lower environmental impact, such as panels made from recycled or recyclable materials, to align with green building practices.
Durability and Longevity:
Assess the expected lifespan of the construction and select materials that offer durability and resistance to environmental factors. This consideration is crucial for minimizing maintenance costs and ensuring the longevity of the structure.
Weight and Load-Bearing Capacity:
The weight of the sandwich panels is a critical factor, especially in projects where load-bearing capacity is a concern. Lightweight panels are advantageous for ease of handling and transportation, particularly in seismic-prone areas.
Fire Resistance:
Different core materials have varying levels of fire resistance. Polyisocyanurate (PIR) panels, for instance, are known for their high resistance to fire. Evaluate the fire safety requirements of the project and choose materials accordingly.
Moisture Resistance:
Moisture ingress can lead to issues such as delamination and reduced insulation effectiveness. Select materials that offer good moisture resistance, particularly in projects where exposure to humidity or water is a concern.
Aesthetic Considerations:
The appearance of the sandwich panels can impact the overall aesthetics of the building. Consider the visual requirements of the project and choose materials that align with the desired architectural design.
Regulatory Compliance:
Ensure that the selected materials comply with building codes and safety regulations. This is crucial for meeting legal requirements and ensuring the safety and reliability of the structure.
Cost Considerations:
Evaluate the overall cost-effectiveness of the materials. While high-quality materials may have a higher initial cost, they can provide long-term benefits in terms of energy savings and reduced maintenance expenses.
Ease of Installation:
Consider the ease of installation when choosing materials. Some materials may require specialized installation techniques, and hiring experienced professionals can be crucial for a successful installation process.
By carefully weighing these considerations, builders and architects can make informed decisions about the selection of sandwich panel materials, ensuring that the chosen panels align with the specific needs and goals of the construction project.
Installation Process of Sandwich Panel Profiles
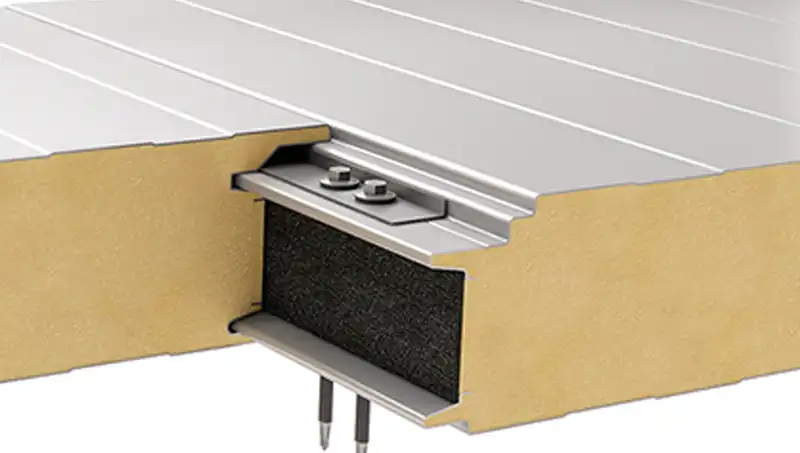

Maintenance and Durability
The longevity of sandwich panel profiles is a key selling point. Routine maintenance, including inspections and repairs, can significantly extend their lifespan. Manufacturers often provide guidelines for upkeep to ensure lasting durability.
Innovations in Sandwich Panel Technology
As technology advances, so does the innovation in sandwich panel profiles. Emerging trends focus on improving energy efficiency, exploring sustainable materials, and enhancing overall performance.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Issues in Profile Panels
Challenges such as delamination, moisture ingress, or inadequate insulation can occur. Identifying these issues early is crucial for implementing effective solutions.
Solutions for Enhanced Performance
From advanced coatings to improved installation techniques, there are solutions available to address common challenges and optimize the performance of sandwich panel profiles.
Cost Analysis of Sandwich Panel Profiles
Initial Costs vs. Long-term Benefits
While the initial costs of sandwich panels may seem higher than traditional materials, the long-term benefits, including energy savings and reduced maintenance, often outweigh the upfront expenses.
Return on Investment Considerations
Investing in high-quality sandwich panel profiles can result in significant long-term returns, making them a wise choice for both residential and commercial construction.
Comparison with Traditional Construction Materials
Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness
Comparisons with traditional materials highlight the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of sandwich panel profiles, making them a competitive option in the construction industry.
Environmental Impact
The environmental footprint of sandwich panels, especially those using sustainable materials, is often lower than that of traditional construction materials, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly practices.
Sandwich Panel Profile FAQs
Are sandwich panels suitable for residential construction?
Yes, sandwich panels are commonly used in residential construction due to their energy efficiency and structural advantages.
What materials are commonly used in sandwich panel profiles?
The most common materials include polyurethane (PU), polyisocyanurate (PIR), and mineral wool.
How do sandwich panels contribute to energy efficiency?
The insulating properties of sandwich panels reduce the need for excessive heating or cooling, resulting in energy savings.
What are the main challenges associated with sandwich panels?
Common challenges include delamination, moisture ingress, and ensuring proper insulation.
Can sandwich panels be used in seismic-prone areas?
Yes, the lightweight nature of sandwich panels makes them suitable for construction in seismic-prone regions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world of construction has been forever transformed by the advent of Sandwich Panel Profiles. Their versatility, energy efficiency, and structural benefits position them as a leading choice for modern architects and builders. Embracing these profiles not only ensures sustainable construction but also paves the way for innovative and resilient structures.




